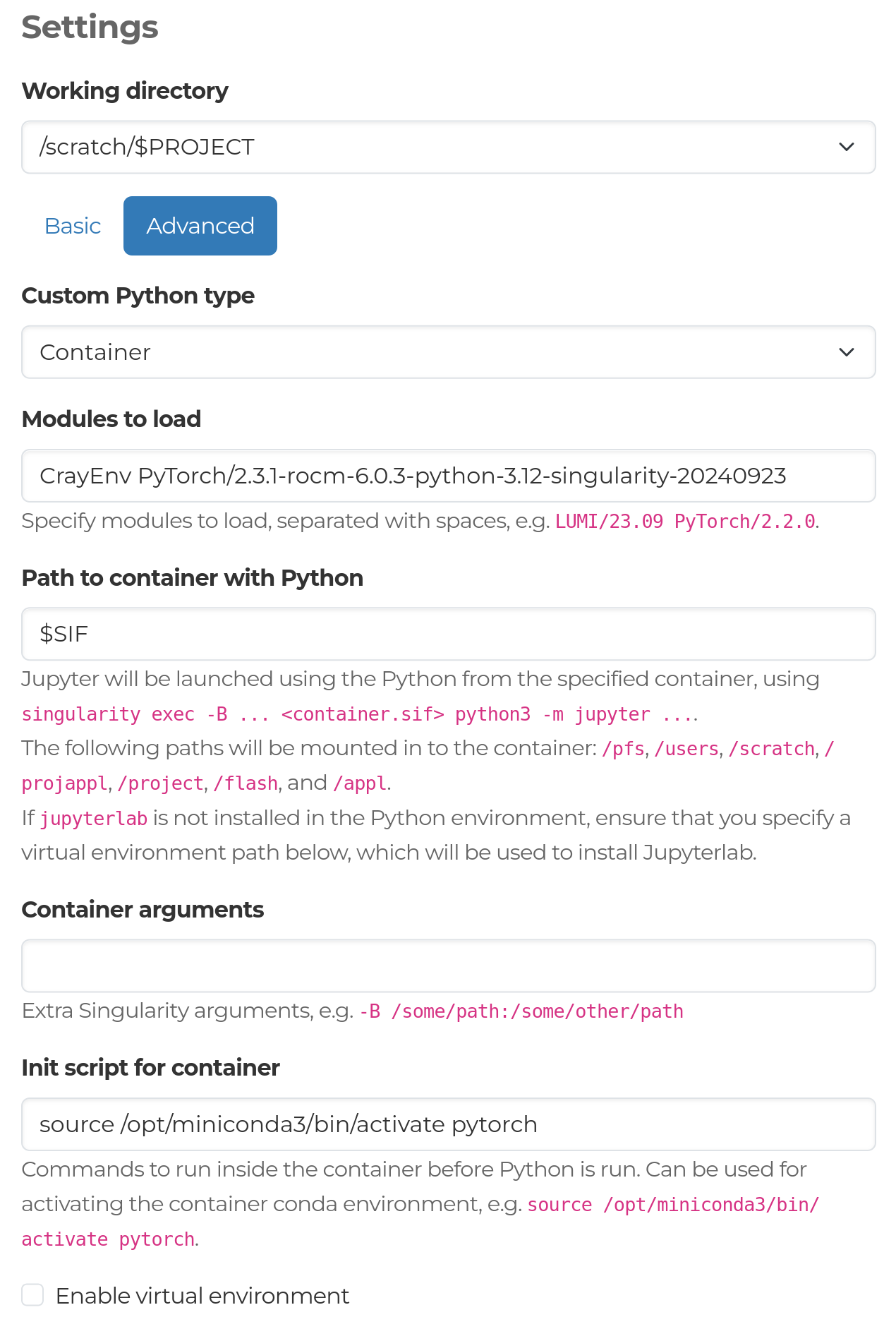
Jupyter
The Jupyter app launches Jupyter Lab on a LUMI compute node, which you can access from the web interface.
In the form you will be able to select:
- Working directory: The directory where your notebook file is stored.
- Basic or Advanced: The Basic setting allows you to use a Python module provided by the system, with either a virtual environment or user-installed packages to extend the module. The Advanced setting lets you set up the Python environment either using a script or a path to a script, as well as use a containerized Python installation. For more details about these, see the sections below.
Basic¶
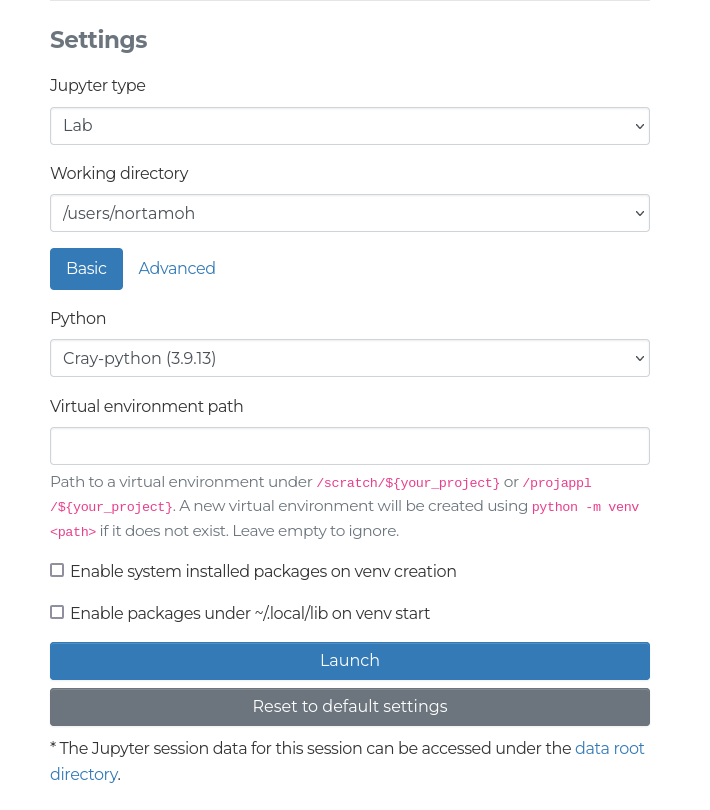
In the basic settings, the following settings are available:
- Python:
Currently, the following Python modules are available:
cray-python,pytorch, andgeoconda. Note thatpytorchandgeocondahave limited support available. You can also select Custom to provide a full path to the Python interpreter you want to use. - Virtual environment: After enabling the use of virtual environment in the form, you can provide a path to your virtual environment. If the provided path does not exist, a new virtual environment using the module, or Python interpreter, selected will be created. If an already existing path is provided, that virtual environment will be used. Note that virtual environments created outside the web interface are not guaranteed to work, so creating your virtual environments in the web interface is recommended. If the field is left empty, no virtual environment is created or used.
- Enable system installed packages on venv creation: If you are basing your Python virtual environment on an existing Python module, you should enable this setting to ensure that you are able to use the Python packages provided by the module. If you are creating a Python environment, and are only using the modules to provide a specific Python version, you can disable this setting.
- Enable packages under ~/.local/lib on venv start:
Enables using packages installed using
pip --user installin virtual environments. It is recommended to leave this disabled to avoid conflicts in package versions.
Advanced¶
In the advanced settings, you can find a dropdown to specify the method for customizing your Python environment:
- Script:
Enter the full script or a path to a script for setting up the environment
to run JupyterLab in the text box. To ensure that Jupyter launches
correctly, ensure that
pythonis available on the path, and thejupyterlabpackage has been installed. Jupyter will be launched using the commandpython -m jupyter lab. - Container: Allows you to use a containerized Python installation. You can specify a list of modules to load before entering the container, the path to your container, additional container launch arguments, as well as an initialization script for the container. A virtual environment can also be used.